Notable Submarine Accidents: Difference between revisions
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) |
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
In 1940, noting with alarm the deteriorating war situation in Europe, orders were issued to reactivate the mothballed O-boats for use as training vessels for the anticipated huge increase in personnel for a rapidly expanding Submarine Service. [[O-9|'''O-9 (SS-70)''']] was one of the boats earmarked for further service. The rushed nature of the order, combined with the large number of subs and ships being pulled out of reserve severely stretched the capabilities of the east coast shipyards. The O-9 needed thorough and meticulous tender-loving-care, but that work was rushed and inadequate, and by the time she was recommissioned in April 1941 she still faced numerous materiel condition challenges. | In 1940, noting with alarm the deteriorating war situation in Europe, orders were issued to reactivate the mothballed O-boats for use as training vessels for the anticipated huge increase in personnel for a rapidly expanding Submarine Service. [[O-9|'''O-9 (SS-70)''']] was one of the boats earmarked for further service. The rushed nature of the order, combined with the large number of subs and ships being pulled out of reserve severely stretched the capabilities of the east coast shipyards. The O-9 needed thorough and meticulous tender-loving-care, but that work was rushed and inadequate, and by the time she was recommissioned in April 1941 she still faced numerous materiel condition challenges. | ||
On June 19, 1941 O-9 got underway from Submarine Base New London and headed out to sea accompanied by her sister boats [[O-6|'''O-6 (SS-67)''']] and [[O-10|'''O-10 (SS-71)''']]. They were to conduct deep submergence trials off the Isle of Shoals in a designated submarine operating area. O-6 and O-10 successfully completed their dives early on the morning of June 20. O-9 dove at 0837 that morning and was never heard from again. She had succumbed to the sea. Her failure to surface was noted by her sister boats at 0940 and the alarm was | On June 19, 1941 O-9 got underway from Submarine Base New London and headed out to sea accompanied by her sister boats [[O-6|'''O-6 (SS-67)''']] and [[O-10|'''O-10 (SS-71)''']]. They were to conduct deep submergence trials off the Isle of Shoals in a designated submarine operating area. O-6 and O-10 successfully completed their dives early on the morning of June 20. O-9 dove at 0837 that morning and was never heard from again. She had succumbed to the sea. Her failure to surface was noted by her sister boats at 0940 and the alarm was sent out. A massive search and rescue operation was immediately begun that including all submarines in the area and the submarine rescue vessels USS Chewink (ASR-3) and the famous Falcon (ASR-2). | ||
Grapnel dragging located the boat on the bottom at the ominous depth of 450 feet. O-9's test depth was only 200 feet. Rescue operations were immediately begun, and divers put over the side. The extreme depth resulted in only two divers making it to the bottom at 432 feet, but they found that the entire after part of the boat from the conning tower aft had imploded, with the front half clearly flooded. The crew was dead. | Grapnel dragging located the boat on the bottom at the ominous depth of 450 feet. O-9's test depth was only 200 feet. Rescue operations were immediately begun, and divers put over the side. The extreme depth resulted in only two divers making it to the bottom at 432 feet, but they found that the entire after part of the boat from the conning tower aft had imploded, with the front half clearly flooded. The crew was dead. | ||
Revision as of 17:32, 10 February 2024
Notes
This section is meant to highlight some of the notable accidents that befell our Submarine Force during the pigboats era. The purpose is to honor the bravery and sacrifice of the men involved, and to show that the Navy persevered and learned from its mistakes. The technology matured and submarines got safer, but sailing a ship under the sea will never be a safe activity. This list is not all-inclusive, nor will it tell the full tale of each incident. It will give an overview and highlight some of the photographs that Ric has collected over the years. Many of these incidents have been covered in depth by other authors, and when possible we will provide links to books that we know will tell the full tale.
For further information on the men who gave their lives in these incidents, we highly recommend the website On Eternal Patrol, or OEP. Charles Hinman and his team have done an amazing job of gathering information on our deceased shipmates. Please take a look.Grampus (Submarine No. 4) and Pike (Submarine No. 6) gasoline fire, September 19, 1908

For a contemporary newspaper article that goes into depth on this incident, please see this link. Note: please disregard the clerical date error at the top of the NHHC photograph. The fire did happen in 1908.
F-4 (Submarine No. 23), Hull failure during a test dive, March 25, 1915

Several months earlier, the boat had been fitted with an experimental propeller design that was intended to provide maximum thrust at low RPM's. When the captain attempted to power out of the uncontrolled descent, the increased RPM's caused the propellers to cavitate badly and lose thrust. When the boat passed crush depth the hull catastrophically imploded and F-4 sank with all hands. There were no survivors.
Five and a half months later, after a herculean effort involving unparalleled bravery and incredible ingenuity, F-4 was raised from 306 feet (92.3 m) of water and returned to Honolulu where she was drydocked and inspected. The remains of her crew were removed and given a hero's procession through Honolulu before they were returned to the mainland for burial. After the completion of the accident investigation, F-4 was stripped of any useful equipment and her hulk was towed to Pearl Harbor where it was dropped in the shallow waters of the then unused Magazine Loch. 25 years later it was found that her wreck was in the way of the rapidly expanding Submarine Base so a trench was dug next to the wreck and she was rolled into it. This got her out of the way and allowed the base to continue its expansion. She remains there to this day, just a few yards off berth S13.
PigBoats.COM is proud to display a collection of photographs of her salvage and those are presented here. In addition, the webmasters provided author Jon Humboldt Gates with technical advice for his book Before the Dolphins Guild which tells the story of the loss of the F-4.A-7 (Submarine No. 8), Gasoline explosion and fire, July 24, 1917

F-1 (Submarine No. 20), Collision with F-3 (Submarine No. 22), December 17, 1917

O-5 (SS-66), Battery explosion, October 5, 1918

S-6 (SS-111), Collision with a destroyer, 1922

O-5 (SS-66), Collision with a merchant ship, October 28, 1923

S-51 (SS-162), Collision with merchant ship, September 25, 1925

In addition, a granddaughter of one of the lost crewmen maintains an excellent informational site on the accident, which can be accessed at the enclosed link.
S-4 (SS-109), Collision with USCGC Paulding, December 17, 1927

Squalus (SS-192), Equipment failure during a test dive, May 23, 1939
What followed was an epic story of the courage and tenacity of our sea service. In the first, and only, operational use of the McCann Rescue Chamber in the USN, all 33 men in the forward compartments were rescued and brought to the surface. Over the next three and a half months the Squalus was salvaged under very difficult conditions and returned to Portsmouth for repair and refurbishment. She was renamed Sailfish (SS-192) and returned to full service. She went on to have a fine war record.
PigBoats.COM has compiled a collection of rescue and salvage photos of this incident and they can be found at this link.
O-9 (SS-70), Hull failure during a test dive, June 20, 1941

In 1940, noting with alarm the deteriorating war situation in Europe, orders were issued to reactivate the mothballed O-boats for use as training vessels for the anticipated huge increase in personnel for a rapidly expanding Submarine Service. O-9 (SS-70) was one of the boats earmarked for further service. The rushed nature of the order, combined with the large number of subs and ships being pulled out of reserve severely stretched the capabilities of the east coast shipyards. The O-9 needed thorough and meticulous tender-loving-care, but that work was rushed and inadequate, and by the time she was recommissioned in April 1941 she still faced numerous materiel condition challenges.
On June 19, 1941 O-9 got underway from Submarine Base New London and headed out to sea accompanied by her sister boats O-6 (SS-67) and O-10 (SS-71). They were to conduct deep submergence trials off the Isle of Shoals in a designated submarine operating area. O-6 and O-10 successfully completed their dives early on the morning of June 20. O-9 dove at 0837 that morning and was never heard from again. She had succumbed to the sea. Her failure to surface was noted by her sister boats at 0940 and the alarm was sent out. A massive search and rescue operation was immediately begun that including all submarines in the area and the submarine rescue vessels USS Chewink (ASR-3) and the famous Falcon (ASR-2).
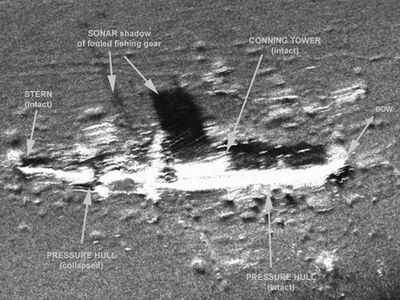
Grapnel dragging located the boat on the bottom at the ominous depth of 450 feet. O-9's test depth was only 200 feet. Rescue operations were immediately begun, and divers put over the side. The extreme depth resulted in only two divers making it to the bottom at 432 feet, but they found that the entire after part of the boat from the conning tower aft had imploded, with the front half clearly flooded. The crew was dead.
The extreme conditions of working at 432 feet forced the commanding officer of the rescue force, Rear Admiral Richard Edwards, to call a halt to the efforts and his decision was backed up by the Secretary of the Navy Frank Knox on June 22. Later that day a solemn funeral service was held aboard the USS Triton (SS-201), one of the accompanying submarines, and the Navy and the nation said farewell to their shipmates. The O-9 and her crew of 33 were left were they laid, and no further attempt was made to salvage her. The cause of her loss was never determined exactly, but it was assumed that it was related to her poor materiel condition. This was not the Navy's finest hour. This loss was likely entirely preventable.
On September 20, 1997 an expedition sponsored by Klein Sonar Systems succeeded in rediscovering the wreck using a towed side-scan sonar system. A subsequent visit to the site by NOAA conducted a thorough sonar survey and they produced the following images.
-
Photo courtesy of Klein Marine Systems via Navsource.
-
Photo courtesy of NOAA.
The site has been designated as an official military burial ground with the exact location held in secret. For information on the O-9's crew, please see the On Eternal Patrol page for the O-9. Rest in peace brothers.
Page created by:
Ric Hedman & David Johnston
1999 - 2023 - PigBoats.COM©
Mountlake Terrace, WA, Norfolk, VA
webmaster at pigboats dot com