Simon Lake non-Navy Submarines: Difference between revisions
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) |
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
To aid in his quest to sell submarines to the USN, Lake also developed the idea of submerging a submarine on a level plane, with a zero angle (sometimes called "even keel diving"). Holland used stern mounted diving planes and the power of the propeller to angle the boat downward and push it under, with surfacing being the opposite operation. Lake felt that this was too dangerous. If the crew lost control of the angle the boat could quickly exceed its hull strength depth and be destroyed. He emphasized the use of multiple sets of planes mounted amidships to ease the boat downward while maintaining a zero angle. This concept ultimately proved to be overly complicated and difficult to execute. The Navy standardized its training on the EB-style angled diving technique, and Lake eventually abandoned zero angle diving. | To aid in his quest to sell submarines to the USN, Lake also developed the idea of submerging a submarine on a level plane, with a zero angle (sometimes called "even keel diving"). Holland used stern mounted diving planes and the power of the propeller to angle the boat downward and push it under, with surfacing being the opposite operation. Lake felt that this was too dangerous. If the crew lost control of the angle the boat could quickly exceed its hull strength depth and be destroyed. He emphasized the use of multiple sets of planes mounted amidships to ease the boat downward while maintaining a zero angle. This concept ultimately proved to be overly complicated and difficult to execute. The Navy standardized its training on the EB-style angled diving technique, and Lake eventually abandoned zero angle diving. | ||
Although a brilliant engineer, Lake possessed two qualities that tended earn him scorn and mistrust rather than the praise and lucrative USN contracts that he desired. He was quite stubborn in his beliefs about how submarines should be operated, and he refused to tolerate any challenge to those ideals. This stubbornness caused him to be quite outspoken when things did not go his way, earning him a reputation as a pariah. Secondly, despite his acknowledged talent as an engineer, Lake was a poor businessman and organizer. His shipyard was chronically underfunded and poorly managed, and thus his profit margin was quite low, and at times non-existent. Despite numerous attempts, Lake was unable to sell a submarine to the USN until 1912. He had been marginally more successful in the overseas market, but he struggled with the USN until this point. The acceptance of his [[G-1|'''submarine G-1''']] seemed to clear the log-jam for a bit, and over the next 10 years he sold a number of boats to the USN. However, the Navy never really liked his designs. They were mechanically and operationally complex, they had features that the Navy didn't like such as midships diving planes and watertight superstructures | Although a brilliant engineer, Lake possessed two qualities that tended earn him scorn and mistrust rather than the praise and lucrative USN contracts that he desired. He was quite stubborn in his beliefs about how submarines should be operated, and he refused to tolerate any challenge to those ideals. This stubbornness caused him to be quite outspoken when things did not go his way, earning him a reputation as a pariah. Secondly, despite his acknowledged talent as an engineer, Lake was a poor businessman and organizer. His shipyard was chronically underfunded and poorly managed, and thus his profit margin was quite low, and at times non-existent. Despite numerous attempts, Lake was unable to sell a submarine to the USN until 1912. He had been marginally more successful in the overseas market, but he struggled with the USN until this point. The acceptance of his [[G-1|'''submarine G-1''']] seemed to clear the log-jam for a bit, and over the next 10 years he sold a number of boats to the USN. However, the Navy never really liked his designs. They were mechanically and operationally complex, they had features that the Navy didn't like such as midships diving planes and watertight superstructures. Because of his poor management his boats were usually very late in delivery and lacking in construction quality. He perpetually struggled to make a profit and was often heavily in debt. Finally tired of his business drama, the USN awarded Lake no more contracts after 1922 and his shipyard went out of business for good in 1924. | ||
Lake continued to be a presence in the submarine engineering community, and he was chosen by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1930 to convert a decommissioned Lake design O-class submarine for an Arctic voyage (see below). Lake's romantic exploration mindset and his Vernian fascination heavily influenced his work on the Arctic submarine, with many of the features and contraptions that he installed being ultimately shown to be impractical or worthless. | Lake continued to be a presence in the submarine engineering community, and he was chosen by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1930 to convert a [[O-12|'''decommissioned Lake design O-class submarine''']] for an Arctic voyage (see below). Lake's romantic exploration mindset and his Vernian fascination heavily influenced his work on the Arctic submarine, with many of the features and contraptions that he installed being ultimately shown to be impractical or worthless. | ||
This page will highlight some of the submarine work that Simon Lake did that ''was not'' accepted by the United States Navy. These boats, although never commissioned as warships in the USN, still were quite important in advancing the state of the art of submarine design and construction in the United States. The submarines that Lake built that were commissioned by the Navy will have their own pages under the Submarine Classes heading. | This page will highlight some of the submarine work that Simon Lake did that ''was not'' accepted by the United States Navy. These boats, although never commissioned as warships in the USN, still were quite important in advancing the state of the art of submarine design and construction in the United States. The submarines that Lake built that were commissioned by the Navy will have their own pages under the Submarine Classes heading. | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 24 April 2024
A brief history of Simon Lake

Lake began his life long pursuit of submarine technology in 1894, when he built his first boat, the wooden hulled, slab-sided Argonaut Junior. He followed this up four years later with the much more advanced metal hulled Argonaut 1. During this time he entered into an intense rivalry with his contemporary John P. Holland to design, build, and sell submarines to a newly interested United States Navy.
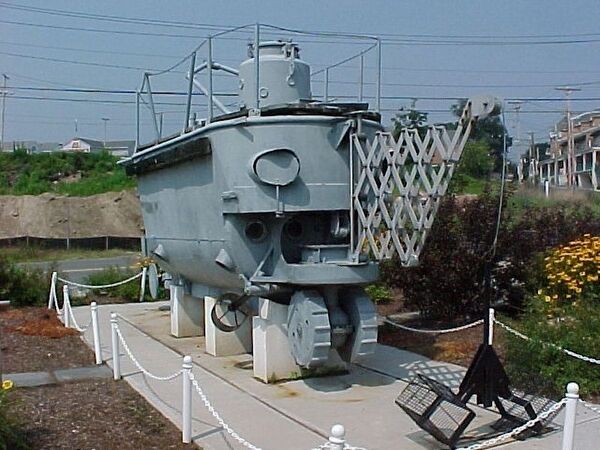
Lake was highly influenced in his work by the Vernian ideals of submarine operations. He saw submarines chiefly in the exploration role, fulfilling a military function only as an aside. His vision had his submarines sailing on the surface to their operating area, diving to the bottom, then rolling along on wheels to a worksite. Suited divers would then emerge from a hatch in the bottom and perform the boat's mission. He was quite stubborn in this vision, and it drove much of his design work. Unfortunately, this vision was not shared by his primary customer, the United States Navy, who understandably saw submarines primarily as a weapon, a mobile minefield upon which an attacking enemy force could be impaled on. Exploration was seen as a secondary role at best. This dichotomy in design philosophy often put Lake and his only real customer at odds with each other.
To aid in his quest to sell submarines to the USN, Lake also developed the idea of submerging a submarine on a level plane, with a zero angle (sometimes called "even keel diving"). Holland used stern mounted diving planes and the power of the propeller to angle the boat downward and push it under, with surfacing being the opposite operation. Lake felt that this was too dangerous. If the crew lost control of the angle the boat could quickly exceed its hull strength depth and be destroyed. He emphasized the use of multiple sets of planes mounted amidships to ease the boat downward while maintaining a zero angle. This concept ultimately proved to be overly complicated and difficult to execute. The Navy standardized its training on the EB-style angled diving technique, and Lake eventually abandoned zero angle diving.
Although a brilliant engineer, Lake possessed two qualities that tended earn him scorn and mistrust rather than the praise and lucrative USN contracts that he desired. He was quite stubborn in his beliefs about how submarines should be operated, and he refused to tolerate any challenge to those ideals. This stubbornness caused him to be quite outspoken when things did not go his way, earning him a reputation as a pariah. Secondly, despite his acknowledged talent as an engineer, Lake was a poor businessman and organizer. His shipyard was chronically underfunded and poorly managed, and thus his profit margin was quite low, and at times non-existent. Despite numerous attempts, Lake was unable to sell a submarine to the USN until 1912. He had been marginally more successful in the overseas market, but he struggled with the USN until this point. The acceptance of his submarine G-1 seemed to clear the log-jam for a bit, and over the next 10 years he sold a number of boats to the USN. However, the Navy never really liked his designs. They were mechanically and operationally complex, they had features that the Navy didn't like such as midships diving planes and watertight superstructures. Because of his poor management his boats were usually very late in delivery and lacking in construction quality. He perpetually struggled to make a profit and was often heavily in debt. Finally tired of his business drama, the USN awarded Lake no more contracts after 1922 and his shipyard went out of business for good in 1924.
Lake continued to be a presence in the submarine engineering community, and he was chosen by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1930 to convert a decommissioned Lake design O-class submarine for an Arctic voyage (see below). Lake's romantic exploration mindset and his Vernian fascination heavily influenced his work on the Arctic submarine, with many of the features and contraptions that he installed being ultimately shown to be impractical or worthless.
This page will highlight some of the submarine work that Simon Lake did that was not accepted by the United States Navy. These boats, although never commissioned as warships in the USN, still were quite important in advancing the state of the art of submarine design and construction in the United States. The submarines that Lake built that were commissioned by the Navy will have their own pages under the Submarine Classes heading.
Argonaut Junior
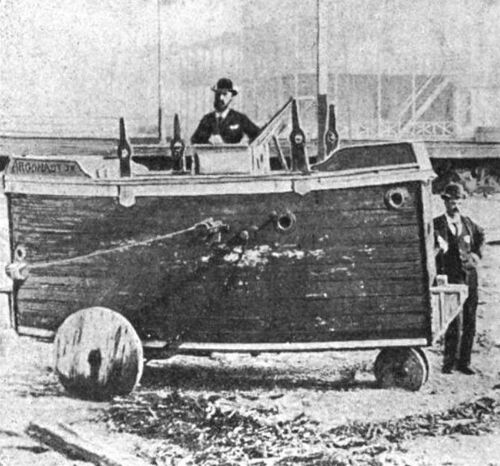
In 2010, an Oklahoma couple built a fully functional replica of the Argonaut Jr. and successfully tested it in a local lake. They did an amazing job for amateurs and their boat looks incredible. For their full story go to their website here.
Photo courtesy of Wikipedia.org
Argonaut 1
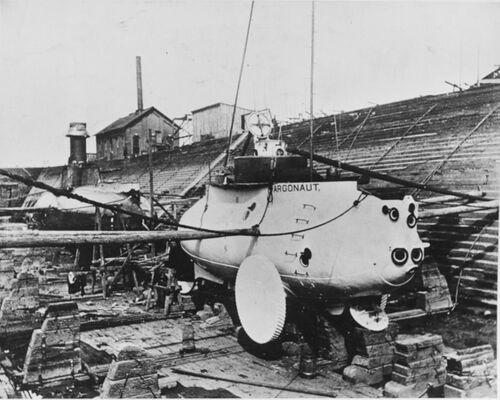
This photo shows Argonaut 1 in drydock at the Columbian Iron Works facility at Locust Point, near Fort McHenry, in Baltimore, Maryland in approximately 1898. The large forward wheels and viewports at the bow are very apparent. Just below the forward viewports is the open diver's hatch.
It is interesting to note that there is another submarine in the dock with the Argonaut. Behind her is the Holland submarine Plunger of 1895, also known as the Holland V. It was an experimental submarine built by Holland under a Navy contract. Steam boiler powered, it was a complete failure and it was never accepted by the Navy or commissioned into service. Never completely finished it lingered at the Holland facility at New Suffolk, NY until it was scrapped in 1917.
Photo NH 57030 courtesy of NHHC.
Protector

This photo was most likely taken shortly after her completion in late 1902. The location is unknown, but is somewhere in the New england area. Note guards at side of vessel to protect the diving planes from damage.
Simon Lake XV/Lake/Defender

This photo shows the Lake moored during the 1906 competition with the Octopus. Her broad, flat deck is quite apparent. Note the unusual oblong torpedo loading hatch and the guard rails protecting the amidships diving planes. She had a helm atop the conning tower and a type of a periscope that Simon Lake called an "omniscope".
This is a very rare photo that is exclusive to PigBoats.COM. Originally it was a postcard that was acquired by Ric Hedman. It had black postal marks on it that partially obscured the image. After being scanned electronically it was painstakingly restored by PigBoats associate Matthew Tripp. The result is an unique look into American submarine history.
Wilkins Arctic Submarine Nautilus (1931)

PigBoats.COM has a collection of drawings and photographs of the boat and the men who sailed her to the Arctic, along with a link to an excellent video that covers the expedition in depth. Those can be found here. In addition, Ric has recreated verbatim a newspaper article written by Sloan Danenhower in March 1931 that describes the technical aspects of the Nautilus and their plans for the voyage.
Explorer
Page created by:
Ric Hedman & David Johnston
1999 - 2023 - PigBoats.COM©
Mountlake Terrace, WA, Norfolk, VA
webmaster@pigboats.com


