G-4: Difference between revisions
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) Added a gallery |
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) Added conning tower photo |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | [[File:New Header G-class.jpg]] | ||
[[File: | <br> | ||
[[File: | === <big>Design and Construction Notes</big> === | ||
[[File:g-4 lines-2.jpg|left|600px]] | |||
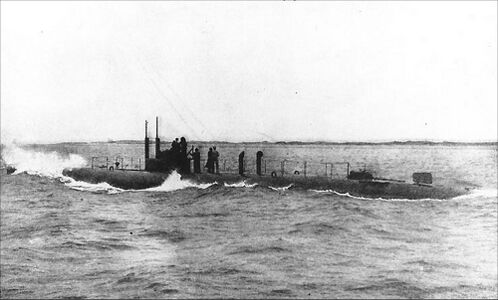
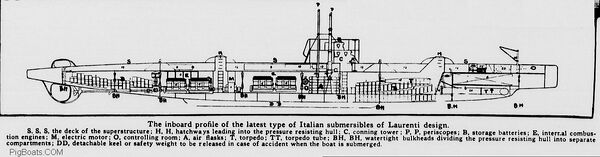
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 was an attempt to introduce competition to the submarine acquisition process in the years immediately before WWI. Authorized in Fiscal Year 1910 along with Lake's Turbot, Thrasher (later G-4) was built to an Italian design by naval architect Cesare Laurenti, whose engineering work for the Italian Navy had gained some recognition in the U.S. This diagram shows the original design by Laurenti, and it had significant differences from the boat that was actually built for the USN. The biggest differences are in the arrangement of the battery wells, the engines, and the aft torpedo tubes. This drawing shows the Laurenti design with the after battery all the way in the stern, ''aft'' of the engines and close to the rudder and stern planes mechanisms. This would prevent the placement of aft torpedo tubes. The original design also shows at least two extra engines and hatches in different locations.<br><br> | |||
The design as built had two forward 18" torpedo tubes that were situated ''below'' the elongated bow, with two more aft under an overhanging flat "shovel" shaped stern. These aft tubes were the very first aft firing tubes in a USN submarine. A large torpedo loading/access hatch was situated above the aft torpedo room, and this hatch had a unique dual hatch/scuttle arrangement common on surface ships but unheard of on [[File:G-4_diagram.jpg|left|600px]]submarines. She had two rudders, one below the stern and a smaller one topside on the aft deck. To accommodate these changes Laurenti removed one set of engines and moved the aft battery well further forward, but unusually, still aft of the motor and engine rooms. There were two removable ventilator pipes above the main motors that had to be rigged manually after surfacing before the engines were started. Above the aft battery well were crew accommodations. The conning tower was half above the engine room and half above the control room, with the hatch leading to it actually in the engine room. The two non-retractable periscopes were forward of the conning tower with the eyepieces letting into the control room. Her forward battery well was partially under both the torpedo room and the control room. She was a full double hull boat, with an inner elliptically shaped, non-circular pressure hull wrapped by a flattened circle-shaped outer hull.<br> | |||
Whether these significant changes in the G-4's internal arrangement reflect a maturation of the Laurenti design, or if they were made at the insistence of the USN before the boat would be built is not known at this time. | |||
Laurenti contracted with the William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Co. in Philadelphia for construction. The design showed some unstable characteristics, as she nearly capsized at launching (see photos below). The Fiat engines, although considered to be reliable, were difficult to maintain and repair due to their metric dimensions and the difficulty in obtaining spare parts from a foreign source. G-4 suffered from numerous mechanical and structural problems and was not considered successful, despite being liked by her crews. She was the only submarine built to a foreign design ever commissioned into the USN. | |||
<small>Drawing by Jim Christley, courtesy of Navsource.org</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
<gallery mode=packed widths=300 heights=200> | <gallery mode=packed widths=300 heights=200> | ||
File:G4-g4launch3-04.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 sliding down the ways at the Cramp yard, August 15, 1912. The strange looking bulge seen on the under-body of the bow just to the right of the diagonal brace is the port torpedo tube. Photo NH 103252 courtesy NHHC</span> | File:G4-g4launch3-04.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 sliding down the ways at the Cramp yard, August 15, 1912. The strange looking bulge seen on the under-body of the bow just to the right of the diagonal brace is the port torpedo tube. Photo NH 103252 courtesy NHHC</span> | ||
File:G4-g4launch31-05.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">This photo was taken a few seconds after the one on the left. The stern has become buoyant and is lifting off the launch cradle. She is starting to lean to port. Photo NH 73380 courtesy of NHHC.</span> | File:G4-g4launch31-05.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">This photo was taken a few seconds after the one on the left. The stern has become buoyant and is lifting off the launch cradle. She is starting to lean to port, most likely do to improperly calculated buoyancy. Photo NH 73380 courtesy of NHHC.</span> | ||
File:G4-g4launch32-06.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">Now with only her bow on the launch cradle, G-4 lists heavily to port. The yard workers topside are scrambling to the starboard side in an attempt to stay aboard | File:G4-g4launch32-06.jpg|<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">Now with only her bow on the launch cradle, G-4 lists heavily to port. The yard workers topside are scrambling to the starboard side in an attempt to stay aboard. National Archives photo.</span> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<br> | |||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">The launch of the G-4 was a near disaster that was narrowly averted. She quickly corrected her list once she was fully off the cradle, but not before two yard workers went into the water and needed to be rescued by a nearby boat. Cramp and the Navy got lucky. It could have been much worse. | |||
Cramp was an experienced shipbuilder whose personnel were very familiar with stability calculations and the physics of floating ship hulls. With that said, the cause of this incident was likely due to the unusual Laurenti design itself, whose stability due to the unusual hull form was questionable. Stability issues would plague G-4 throughout her operational career. She was hard to sail properly, proving difficult for her crew to handle both surfaced and submerged. | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
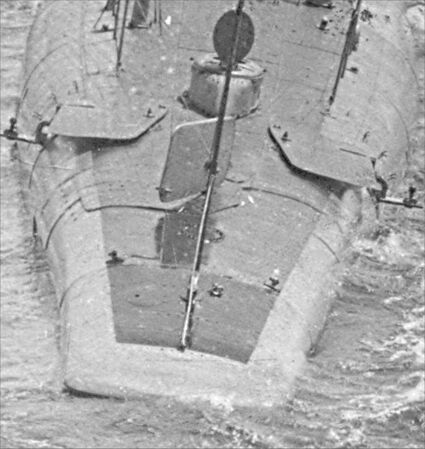
[[File:G4-g4top-07.jpg|left| | [[File:G4-g4top-07.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 at the Cramp yard during her | <div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 at the Cramp yard during her fitting out period, fall of 1912. This is a good overhead view of some of her more unusual features. The bow planes lay flat on the fore deck. They fold out and down and lock on to an axle that then rotates the planes to dive and rise positions. Although hard to see at the stern, the stern planes operate like the bow planes and are partly extended. The port plane can be seen as a square shape just forward of the "doghouse" on the stern. The starboard plane is actually seen edge on, but its reflection can be seen in the water and you can se its square shape there. In the fully extended position both sets of planes would be flat to the water. Cramp yard slipways can be seen in the background. | ||
<small>National Archives photo.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
[[File:G-4_fittingout.jpg|left| | |||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 | [[File:G-4_fittingout.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">G-4 on October 2, 1912, at the Cramp yard going through her fitting out period, with this photo likely taken at about the same time as the one above. During this post-launch phase of her construction she will receive a majority of her piping, electrical and internal systems, and habitability features. On the right near the bow the anchor hawse pipe can be seen, with an anchor chain running aft into an enclosed locker. This locker housed the anchor itself, attached to a "billboard" style release mechanism. The locker doors had to be opened to release the anchor. Billboard style anchor mounts were common on surface ships of this time, but very unusual on submarines. | |||
<small>Photo NH 43799 courtesy of the Naval History & Heritage Command.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
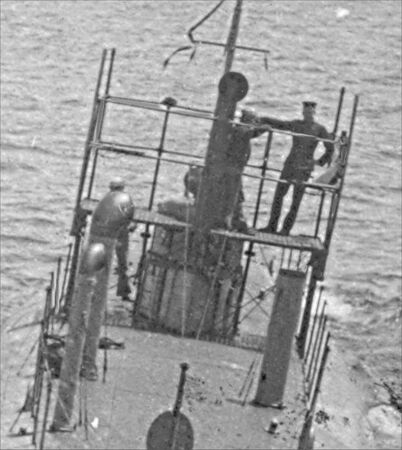
[[File:G-4 conning tower Oct 2 1912A.jpg|left|500px]] | |||
A closeup of the G-4's conning tower taken on the same day as the photo above. This photo highlights the unusual configuration of the conning tower. The two non-retractable periscopes are ''forward'' of the conning tower itself, with both of them having their eyepieces in the control room. The center part of the tower is actually above the engine room, with the hatch leading to it accessed from the engine room. Thick rectangular deadlight windows are situated on the sides of the tower, giving the conning officer some level of visibility while submerged or awash. | |||
At the aft end is the large main induction pipe for the four engines below. Between the pipe and the conning tower is a surface steering station. It has a horizontal handwheel attached to a long rod that penetrates down into the engine room, connecting via a universal joint to a horizontal rod that runs aft to the rudder gearing. There is also a steering station below in the control room that is connected to the same horizontal rod. | |||
The number "41" is not the boat's hull number. Vertically arranged numbers were used in the early days on submarines as visual expedients to place the boat within a steaming formation while on the surface. Their use was discontinued during WWI as they were easily confused as the boat's actual hull number. | |||
<small>NARA photo via historylink101.com.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | |||
[[File:G4-g4workers10301912-08.jpg|left|500px]] | |||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">A few of the workmen from the Cramp yard that built the G-4. Seen here are yard officials, shop and department supervisors, and the craftsmen who were putting the G-4 together. Commissioning was still 14 months away. | |||
<small>Photo NH 73381 courtesy NHHC.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | |||
<gallery mode=packed widths=400 heights=300> | <gallery mode=packed widths=400 heights=300> | ||
File:G4-g4atsea-11.jpg | File:G4-g4atsea-11.jpg | ||
File:G4-g4atsea2-12.jpg | File:G4-g4atsea2-12.jpg | ||
File:G4-g4atsea3-13.jpg | File:G4-g4atsea3-13.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
A nice photo of G-4 from the stern at sea prior to WW I, approximately 1914, along with two closeups. The position of the upper rudder says that the submarine is making a left turn, and this could explain the starboard list, although G-4 was known to have stability issues. The middle picture is a closeup of the stern, showing details of the topside rudder, folded up stern planes, and the open aft torpedo room hatch. Both the stern and bow diving planes had to be manually rigged out by sending a crewman topside prior to diving, with that same crewman taking down and stowing the topside ventilation pipes. This was a dangerous evolution in anything other than a calm sea. The third photo is a closeup of the conning tower fairwater and bridge structure. The commissioning pennant is flying from the radio mast. The officer on the right is most likely the boat's Commanding Officer, LT Ernest D. McWhorter, a Navy Cross awardee later in WWI. | |||
<small>Photo from the Rick Larson Collection, now in the private collection of Ric Hedman.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
<gallery mode=packed widths= | |||
File:G4-g4atsea-09.jpg | <gallery mode="packed" widths=300 heights=200> | ||
File:G4-g4atsea2-10.jpg | File:G4-g4atsea-09.jpg | ||
File:G4-g4atsea2-10.jpg | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Two photos of G-4 at sea, most likely pre-WW I, circa 1914-15. Note the Allied signal bell on the fore deck aft of the hatch and the upper rudder all the way to the right, behind the two men. In the second photo, taken shortly after the first one, G-4 is burying her bow in a head sea. The bow is to the left in these photos, and the unusual arrangement of her periscopes, forward of the conning tower fairwater, is plainly visible. | |||
<small>National Archives photos.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | |||
[[File:G4-g4crew1917-14.jpg|left|500px]] | |||
<div style="text-align: justify;"><span style="color:#00008B">Ship's officers and crew posed on deck, 1917. G-4 was operating out of Submarine Base New London, CT. at the time. The two officers (4th & 5th from left, front row) are LT(jg) Paul F. Foster (Commanding Officer) and LT(jg) William F. Callaway (Executive Officer). | |||
<small>National Archives photo.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
[[File:G4- | [[File:G4-g4a-17.jpg|left|400px]] | ||
One of G-4's crew whose name has unfortunately been lost to the ages. He is in his dress blues, wearing the traditional "flat hat" with the G-4 name on it. The rate insignia on his left arm is unclear, but it may be for a Machinist Mate or Motor Machinist Mate 1st Class. His spirits are obviously high, with a self-assured smile and a countenance of confidence that is the hallmark of a sailor Qualified in Submarines. | |||
<small>Photo in the private collection of Ric Hedman</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
File: | [[File:Crew-enspaulwfoster-001.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
</ | Ensign Paul Frederick Foster, USN, photographed circa 1914. Foster was born on March 25, 1889 in Wichita, Kansas. He received a senatorial appointment from the state of Idaho to the U.S. Naval Academy. Following graduation in 1911, he served on the cruiser [https://www.navsource.org/archives/04/acr11/acr11.htm '''Washington (Armored Cruiser No. 11)'''] and the battleship [http://www.navsource.org/archives/01/31a.htm '''Utah (BB-31)'''] as a midshipman. In March 1912, was commissioned as an Ensign. On 21-22 April 1914, Foster participated at the intervention at Vera Cruz, Mexico, leading his landing company with skill and courage. For his "distinguished conduct in battle", he was awarded the Medal of Honor. | ||
After submarine instruction on board the auxiliary cruiser [http://www.navsource.org/archives/09/03/0305.htm '''USS Prairie'''], he reported on board the G-4. In March 1915, Foster was promoted to Lieutenant Junior Grade and, in early 1916, was given command of G-4. | |||
Relocating to Ireland in December 1917, he was assigned to the submarine tender [https://www.navsource.org/archives/09/36/3602.htm '''Bushnell (Submarine Tender No. 2)'''] in Bantry Bay, Ireland. Foster was temporarily promoted to Lieutenant in May 1918. While serving in Irish waters, he took command of the submarine [[L-2|'''L-2 (Submarine No 41)''']]. Lieutenant Foster was awarded the Distinguished Service Medal for his role in the sinking of the German submarine UB-65 off the Irish coast on 10 July 1918.</span><br> | |||
<small>National Archives photo.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
[[File:G4-g4foster-15.jpg|left|500px]] | |||
Photographed looking aft on board the G-4, Commanding Officer LT(jg) Paul F. Foster, circa 1915-1916. G-4 looks to be a wet boat on the surface. There is a stiff breeze blowing to port, and Foster stands with a stance typical of an experienced sailor, braced against the boat's roll and against the breeze. | |||
<small>National Archives photo.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
[[File:6a-g-4.jpg|left|500px]] | |||
File:6a-g-4.jpg| | |||
G-4's officers standing beside their boat at Submarine Base New London, CT. in 1917. They are LT(jg) William F. Callaway (Executive Officer), at left, and LT(jg) Paul F. Foster (Commanding Officer). | |||
<small>National Archives photo.</small> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | [[File:Red bar sub new 2.jpg]] | ||
<center>[[G-class|Return to the G-class page]] | [[Submarine Classes|Return to the Submarine Classes page]]</center> | |||
[[File:Red bar sub new.jpg]] | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
Page created by:<br> | Page created by:<br> | ||
<small>David Johnston | <small>Ric Hedman & David Johnston<br> | ||
1999 - 2023 | 1999 - 2023 - PigBoats.COM<sup>©</sup><br> | ||
PigBoats.COM<sup>©</sup><br> | Mountlake Terrace, WA, Norfolk, VA<br> | ||
Mountlake Terrace, WA | [mailto:webmaster@pigboats.com '''webmaster@pigboats.com''']</small> | ||
Norfolk, VA<br> | |||
webmaster | |||
</center> | </center> | ||
[[File:Subs bottom line 2.jpg]] | [[File:Subs bottom line 2.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:48, 22 March 2025
Design and Construction Notes
The design as built had two forward 18" torpedo tubes that were situated below the elongated bow, with two more aft under an overhanging flat "shovel" shaped stern. These aft tubes were the very first aft firing tubes in a USN submarine. A large torpedo loading/access hatch was situated above the aft torpedo room, and this hatch had a unique dual hatch/scuttle arrangement common on surface ships but unheard of on
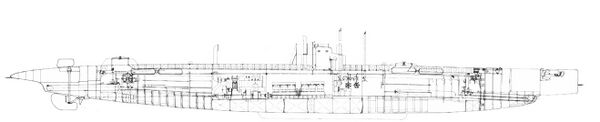
Whether these significant changes in the G-4's internal arrangement reflect a maturation of the Laurenti design, or if they were made at the insistence of the USN before the boat would be built is not known at this time.
Laurenti contracted with the William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Co. in Philadelphia for construction. The design showed some unstable characteristics, as she nearly capsized at launching (see photos below). The Fiat engines, although considered to be reliable, were difficult to maintain and repair due to their metric dimensions and the difficulty in obtaining spare parts from a foreign source. G-4 suffered from numerous mechanical and structural problems and was not considered successful, despite being liked by her crews. She was the only submarine built to a foreign design ever commissioned into the USN.
Drawing by Jim Christley, courtesy of Navsource.org
-
G-4 sliding down the ways at the Cramp yard, August 15, 1912. The strange looking bulge seen on the under-body of the bow just to the right of the diagonal brace is the port torpedo tube. Photo NH 103252 courtesy NHHC
-
This photo was taken a few seconds after the one on the left. The stern has become buoyant and is lifting off the launch cradle. She is starting to lean to port, most likely do to improperly calculated buoyancy. Photo NH 73380 courtesy of NHHC.
-
Now with only her bow on the launch cradle, G-4 lists heavily to port. The yard workers topside are scrambling to the starboard side in an attempt to stay aboard. National Archives photo.
Cramp was an experienced shipbuilder whose personnel were very familiar with stability calculations and the physics of floating ship hulls. With that said, the cause of this incident was likely due to the unusual Laurenti design itself, whose stability due to the unusual hull form was questionable. Stability issues would plague G-4 throughout her operational career. She was hard to sail properly, proving difficult for her crew to handle both surfaced and submerged.

National Archives photo.

Photo NH 43799 courtesy of the Naval History & Heritage Command.

A closeup of the G-4's conning tower taken on the same day as the photo above. This photo highlights the unusual configuration of the conning tower. The two non-retractable periscopes are forward of the conning tower itself, with both of them having their eyepieces in the control room. The center part of the tower is actually above the engine room, with the hatch leading to it accessed from the engine room. Thick rectangular deadlight windows are situated on the sides of the tower, giving the conning officer some level of visibility while submerged or awash.
At the aft end is the large main induction pipe for the four engines below. Between the pipe and the conning tower is a surface steering station. It has a horizontal handwheel attached to a long rod that penetrates down into the engine room, connecting via a universal joint to a horizontal rod that runs aft to the rudder gearing. There is also a steering station below in the control room that is connected to the same horizontal rod.
The number "41" is not the boat's hull number. Vertically arranged numbers were used in the early days on submarines as visual expedients to place the boat within a steaming formation while on the surface. Their use was discontinued during WWI as they were easily confused as the boat's actual hull number.
NARA photo via historylink101.com.
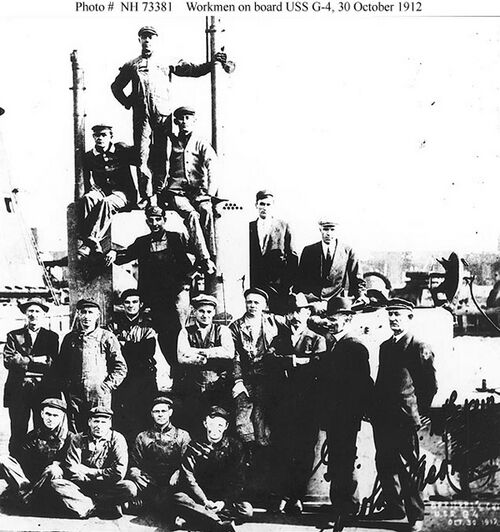

Photo NH 73381 courtesy NHHC.
A nice photo of G-4 from the stern at sea prior to WW I, approximately 1914, along with two closeups. The position of the upper rudder says that the submarine is making a left turn, and this could explain the starboard list, although G-4 was known to have stability issues. The middle picture is a closeup of the stern, showing details of the topside rudder, folded up stern planes, and the open aft torpedo room hatch. Both the stern and bow diving planes had to be manually rigged out by sending a crewman topside prior to diving, with that same crewman taking down and stowing the topside ventilation pipes. This was a dangerous evolution in anything other than a calm sea. The third photo is a closeup of the conning tower fairwater and bridge structure. The commissioning pennant is flying from the radio mast. The officer on the right is most likely the boat's Commanding Officer, LT Ernest D. McWhorter, a Navy Cross awardee later in WWI.
Photo from the Rick Larson Collection, now in the private collection of Ric Hedman.
Two photos of G-4 at sea, most likely pre-WW I, circa 1914-15. Note the Allied signal bell on the fore deck aft of the hatch and the upper rudder all the way to the right, behind the two men. In the second photo, taken shortly after the first one, G-4 is burying her bow in a head sea. The bow is to the left in these photos, and the unusual arrangement of her periscopes, forward of the conning tower fairwater, is plainly visible.
National Archives photos.

National Archives photo.
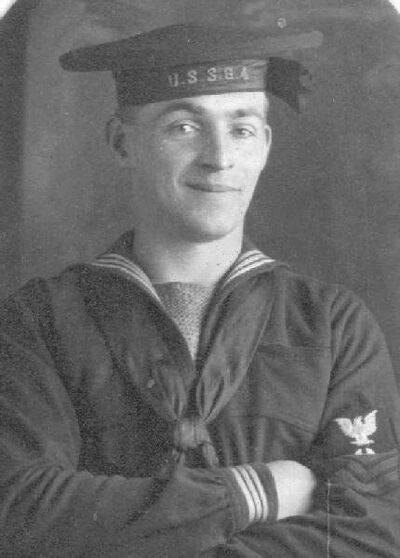

One of G-4's crew whose name has unfortunately been lost to the ages. He is in his dress blues, wearing the traditional "flat hat" with the G-4 name on it. The rate insignia on his left arm is unclear, but it may be for a Machinist Mate or Motor Machinist Mate 1st Class. His spirits are obviously high, with a self-assured smile and a countenance of confidence that is the hallmark of a sailor Qualified in Submarines.
Photo in the private collection of Ric Hedman
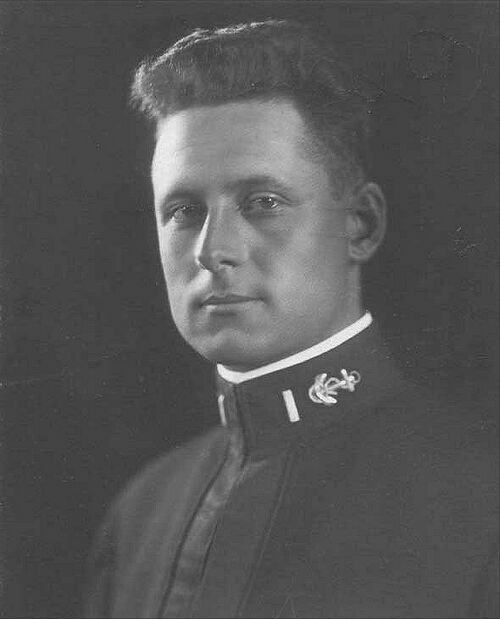

Ensign Paul Frederick Foster, USN, photographed circa 1914. Foster was born on March 25, 1889 in Wichita, Kansas. He received a senatorial appointment from the state of Idaho to the U.S. Naval Academy. Following graduation in 1911, he served on the cruiser Washington (Armored Cruiser No. 11) and the battleship Utah (BB-31) as a midshipman. In March 1912, was commissioned as an Ensign. On 21-22 April 1914, Foster participated at the intervention at Vera Cruz, Mexico, leading his landing company with skill and courage. For his "distinguished conduct in battle", he was awarded the Medal of Honor.
After submarine instruction on board the auxiliary cruiser USS Prairie, he reported on board the G-4. In March 1915, Foster was promoted to Lieutenant Junior Grade and, in early 1916, was given command of G-4.
Relocating to Ireland in December 1917, he was assigned to the submarine tender Bushnell (Submarine Tender No. 2) in Bantry Bay, Ireland. Foster was temporarily promoted to Lieutenant in May 1918. While serving in Irish waters, he took command of the submarine L-2 (Submarine No 41). Lieutenant Foster was awarded the Distinguished Service Medal for his role in the sinking of the German submarine UB-65 off the Irish coast on 10 July 1918.
National Archives photo.
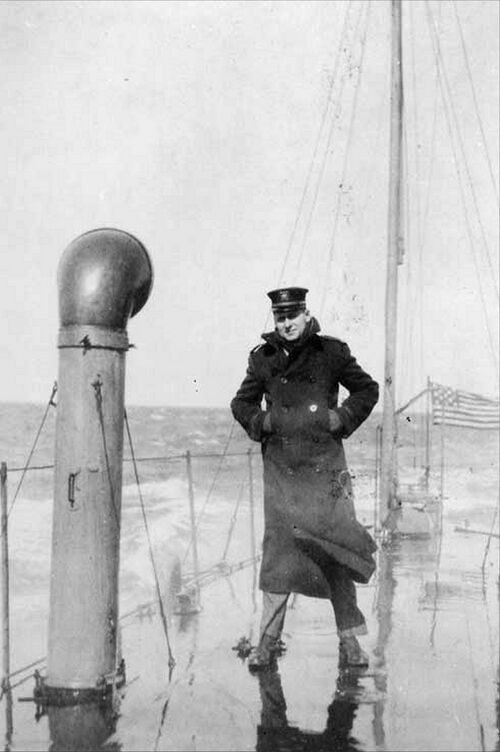

Photographed looking aft on board the G-4, Commanding Officer LT(jg) Paul F. Foster, circa 1915-1916. G-4 looks to be a wet boat on the surface. There is a stiff breeze blowing to port, and Foster stands with a stance typical of an experienced sailor, braced against the boat's roll and against the breeze.
National Archives photo.
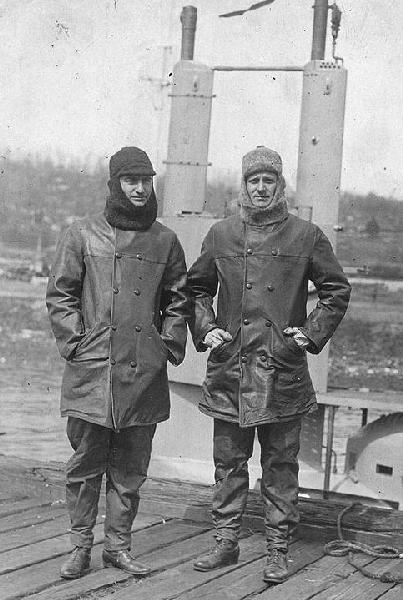

G-4's officers standing beside their boat at Submarine Base New London, CT. in 1917. They are LT(jg) William F. Callaway (Executive Officer), at left, and LT(jg) Paul F. Foster (Commanding Officer).
National Archives photo.
Page created by:
Ric Hedman & David Johnston
1999 - 2023 - PigBoats.COM©
Mountlake Terrace, WA, Norfolk, VA
webmaster@pigboats.com