Holland Torpedo Boat Company Station: Difference between revisions
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) m (Adding text) |
Pbcjohnston (talk | contribs) (Added picture and text) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The site stayed in the Tuthill family and continued to operate as a boatyard and eventually an oil distribution site. The family sold off the oil business in 1976. Mr. J. Arthur Kenniff had purchased the boatyard portion in 1960 and built and repaired boats there until at least 1983. Eventually the site came under the ownership of the local Cuthogue/New Suffolk government. There was a plan at one point of developing the site with condos, but that never came to pass. Today, the site is called "The New Suffolk Waterfront", with the old Holland basin the mooring site of several small yachts and boats. | The site stayed in the Tuthill family and continued to operate as a boatyard and eventually an oil distribution site. The family sold off the oil business in 1976. Mr. J. Arthur Kenniff had purchased the boatyard portion in 1960 and built and repaired boats there until at least 1983. Eventually the site came under the ownership of the local Cuthogue/New Suffolk government. There was a plan at one point of developing the site with condos, but that never came to pass. Today, the site is called "The New Suffolk Waterfront", with the old Holland basin the mooring site of several small yachts and boats. | ||
Today, New Suffolk has reverted to its pre-Holland 1899 ideal. The town is charming and quaint, with modest but stately homes gracing the hilly streets. Life seems to run at a slower pace there, and the approximately 500 residents seem to like it that way. | [[File:New Suffolk 2024 waterfront.JPG|275px|thumb|right|<small>Photo by Dave Johnston, May 2024</small>]] Today, New Suffolk has reverted to its pre-Holland 1899 ideal. The town is charming and quaint, with modest but stately homes gracing the hilly streets. Life seems to run at a slower pace there, and the approximately 500 residents seem to like it that way. As far as can be determined, no buildings from either the Goldsmith & Tuthill days or the HTBC residency remain. However, this is one building at the northern corner of the basin that bears a resemblance to the old machine shop building. | ||
Revision as of 20:13, 18 June 2024
The Holland Torpedo Boat Company Station
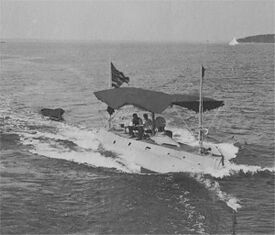

The trials of the Holland VI on Great Peconic Bay were entirely successful and after a haulout for minor modifications and repairs at Greenport, NY and one more trial run the boat was finally purchased by the Navy in April, 1900 and commissioned as the Holland in October. Electric Boat, however, was already looking to the future. Entirely at their own expense they contracted with Crescent Shipyard to build a larger and improved version of the Holland, with the intent of using her as a demonstration model for seven copies that Rice was working diligently to get the Navy to purchase. This new boat, called Fulton, was quickly moved to New Suffolk for testing and demonstration trials. The Fulton trials were entirely successful and they cleared the bureaucratic logjam around the authorization for the seven Adder-class submarines, five of which quickly followed the Fulton to New Suffolk (two of them were built in San Francisco).
-
The EB/HTBC facility at New Suffolk. The tug Kelpie is in the foreground, with the hulk of the 1895 Plunger moored ahead of it. In the background a several of the Adder-class submarines. Note the sign on the roof of the machine shop/draftsman's shop.
-
Several of the Adder-class boats moored at the northern corner of the basin. Moccasin (Submarine No. 5) is in the right background.
-
A view looking back from about half-way down the quay wall. Adder (Submarine No. 3) is in the background.
Fulton, Adder, Plunger, Moccasin, Porpoise, and Shark were joined in New Suffolk by a company owned tugboat called the Kelpie, which accompanied the boats as they made their initial trial runs in Great Peconic Bay. In addition, the hulk of a never completed steam powered submarine contracted to Holland's company in 1895 (also called the Plunger) was towed up to the station and moored to the quay wall inside the basin. Sleepy little New Suffolk became a busy and prosperous place for several years, with the new Adder-class submarines arriving regularly and trials being run out in the bay. New Suffolk was far enough away from New York City to keep the public and press at bay, but Rice was savvy enough to understand the advantages of getting favorable publicity and thus selected members of the press were often invited out to view the comings and goings around the station. The nearby southern shore of Long Island was also becoming a popular destination for summer vacations of the New York elite, and thus viewing the submarine movements became a favored pastime for Rice's urban colleagues. In addition, many high ranking Naval officers visited the site to see how the boats performed. Of course, the town played host to the incoming crews of the new submarines.

The site stayed in the Tuthill family and continued to operate as a boatyard and eventually an oil distribution site. The family sold off the oil business in 1976. Mr. J. Arthur Kenniff had purchased the boatyard portion in 1960 and built and repaired boats there until at least 1983. Eventually the site came under the ownership of the local Cuthogue/New Suffolk government. There was a plan at one point of developing the site with condos, but that never came to pass. Today, the site is called "The New Suffolk Waterfront", with the old Holland basin the mooring site of several small yachts and boats.

Page created by:
Ric Hedman & David Johnston
1999 - 2023 - PigBoats.COM©
Mountlake Terrace, WA, Norfolk, VA
webmaster@pigboats.com



